Suspendable Hydrogel Nanovials for Massively Parallel Single-Cell Functional Analysis and Sorting
Joseph de Rutte, Robert Dimatteo, Maani M. Archang, Mark van Zee, Doyeon Koo, Sohyung Lee, Allison C. Sharrow, Patrick J. Krohl, Michael Mellody, Sheldon Zhu, James V. Eichenbaum, Monika Kizerwetter, Shreya Udani, Kyung Ha, Richard C. Willson, Andrea L. Bertozzi, Jamie B. Spangler, Robert Damoiseaux, and Dino Di Carlo
ACS Nano, Mar 2022
Abstract
Techniques to analyze and sort single cells based on functional outputs, such as secreted products, have the potential to transform our understanding of cellular biology as well as accelerate the development of next-generation cell and antibody therapies. However, secreted molecules rapidly diffuse away from cells, and analysis of these products requires specialized equipment and expertise to compartmentalize individual cells and capture their secretions. Herein, we describe methods to fabricate hydrogel-based chemically functionalized microcontainers, which we call nanovials, and demonstrate their use for sorting single viable cells based on their secreted products at high-throughput using only commonly accessible laboratory infrastructure. These nanovials act as solid supports that facilitate attachment of a variety of adherent and suspension cell types, partition uniform aqueous compartments, and capture secreted proteins. Solutions can be exchanged around nanovials to perform fluorescence immunoassays on secreted proteins. Using this platform and commercial flow sorters, we demonstrate high-throughput screening of stably and transiently transfected producer cells based on relative IgG production. Chinese hamster ovary cells sorted based on IgG production regrew and maintained a high secretion phenotype over at least a week, yielding >40% increase in bulk IgG production rates. We also sorted hybridomas and B lymphocytes based on antigen-specific antibody production. Hybridoma cells secreting an antihen egg lysozyme antibody were recovered from background cells, enriching a population of ∼4% prevalence to >90% following sorting. Leveraging the high-speed sorting capabilities of standard sorters, we sorted >1 million events in <1 h. IgG secreting mouse B cells were also sorted and enriched based on antigen-specific binding. Successful sorting of antibody-secreting B cells combined with the ability to perform single-cell RT-PCR to recover sequence information suggests the potential to perform antibody discovery workflows. The reported nanovials can be easily stored and distributed among researchers, democratizing access to high-throughput functional cell screening.
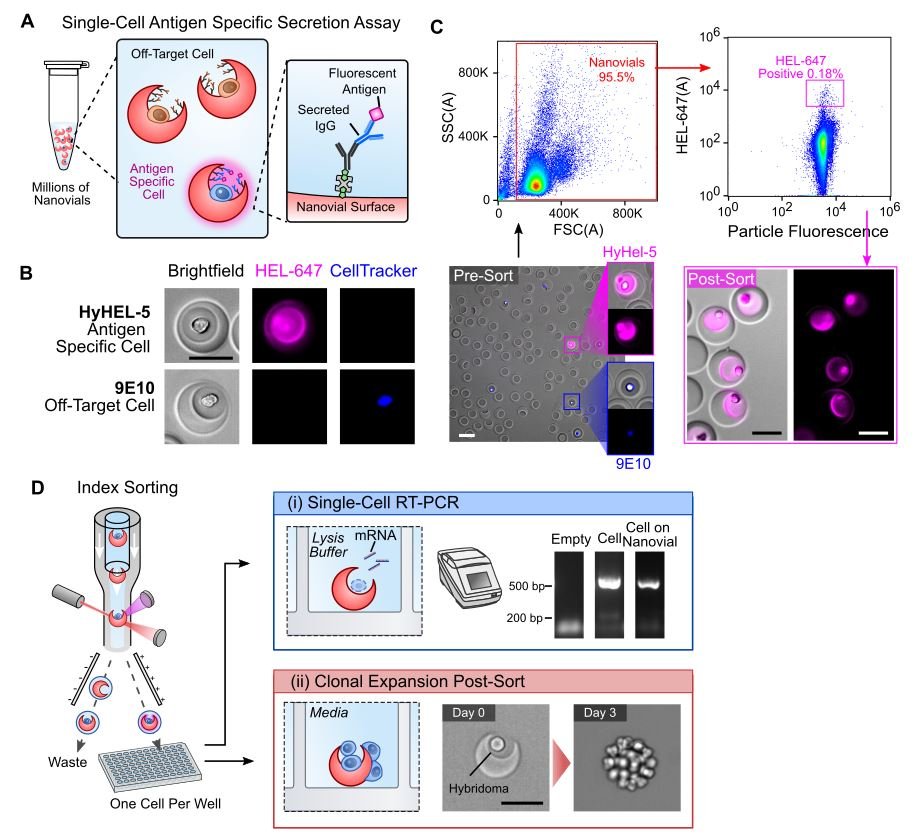
Detection and sorting of antigen-specific antibody secreting cells.
(A) Hybridomas or B cells loaded into nanovials secrete antibodies which are captured onto the nanovial surface via biotinylated capture antibodies. Captured IgG is then labeled with fluorescent antigen to assess specificity of the secreted IgG. (B) Fluorescence microscopy images reveal specific signal from binding to Alexa Fluor™ 647 conjugated hen egg lysozyme (HEL-647) on nanovials containing a hybridoma line (HyHEL-5) secreting IgG HEL while a cell line (9E10) secreting an off-target IgG results in no signal. (C) HyHel-5 hybridomas spiked into 9E10 hybridomas (CellTracker™ Blue) at a 1:25 ratio were assayed by fluorescence microscopy for HEL-specific signal before FACS sorting (Pre-Sort) and after sorting using a high HEL-AF647 gate (Post-Sort). A table showing the Pre-Sort and Post-Sort statistics is shown. (D) Using the index sorting function of the flow cytometer we sorted single hybridomas loaded onto nanovials and (i) demonstrate that RNA can be reverse transcribed and amplified from single cells loaded on nanovials at comparable rates to single cells sorted that were freely suspended. A gel band corresponding to the correct heavy chain amplicon length is observed. (ii) We additionally demonstrate that individual hybridomas can be expanded into a clonal colony directly from the nanovials following sorting.
Topics
Antibody Discovery, Cell Line Development, Technology, Workflow Improvement, Theory
Cell Types
Mouse B Cells, Hybridomas, CHO Cells, HEK293
Flow Cytometers
SONY SH800, On-Chip Sort, Biosorter
Related Products