FAQ
1. Introduction and Basics
What are Nanovials?
Nanovials are tiny hydrogel particles that act like mini suspendable wells for cells.
Each Nanovial:
Holds a single cell or a small group of cells in a nanoliter-sized cavity
Has an inner surface that can be functionalized with biotin, ECM, antibodies, or antigens to capture cells and what they secrete
Can be run on standard flow cytometers and cell sorters, so you can measure secretions, surface markers, sequences and other readouts together.
How do Nanovials work?
Here is a typical workflow:
Load cells into Nanovials: Cells are mixed with Nanovials so that each cavity holds a single cell or multiple cells (for interaction assays). Cells are held in place on the Nanovial surface by binding to a cell capture antibody, ECM in the cavity, or other specificity markers (e.g., peptide–MHC, antigen).
Let cells interact and/or secrete, and capture signals: The inner surface of the Nanovial can be coated with capture molecules (such as antibodies or antigens), or you can present targets on other cells co-loaded in the same Nanovial.
In secretion assays, proteins like antibodies or cytokines are captured on the Nanovial surface around the cell.
In cell–cell interaction assays, the key readout may instead be what happens to the partner cell (e.g., antibody binding, activation markers, reporter signal), even if secretion is not the primary focus.
Stain and detect by flow cytometry: Fluorescent detection antibodies are added to label captured secretions or interaction-dependent signals. Nanovials containing “active” cells or cell pairs will be fluorescent, while inactive ones remain dim. Additional cell surface markers can be included to increase specificity during flow cytometry or sorting.
Analyze and sort: Nanovials are run on a standard flow cytometer or cell sorter, where you can:
Measure secretion levels, interaction readouts, and surface markers at the same time
Sort the best-secreting, most activated, or otherwise interesting cells or cell pairs, while keeping them alive for downstream culture, sequencing, or further assays.
2. Applications and Use Cases
What types of applications can Nanovials be used for?
Nanovials are used for functional single-cell and multicell assays. Typical applications include:
Single-cell antibody discovery: Identify antigen-specific, high-producing plasma B cells or hybridomas.
Cell therapy development & QC: Characterize CAR-Ts based on function or enrich for top EV-secreting cells.
Cytokine and secretome profiling: Load T cells (or other immune cells) and measure their secreted cytokines.
Cell line development: Isolate the most productive clones from mixed populations.
Cell–cell interaction studies: Co-load two or more cell types in the same Nanovial to study binding, activation, or killing.
What Nanovial sizes do you offer, and how are they typically used?
Nanovials come in two sizes:
35 µm – typically used for single cell assays
50 µm – typically used for multicell assays where you want two or more cells in the same Nanovial
Which Nanovial product is right for my application?
Nanovials come in multiple flexible formats to support different applications:
Biotinylated Nanovials – Our most flexible format, you bring your own antibodies and reagents.
Developer Kits – Pair Nanovials with validated cell capture antibodies to help you jumpstart custom workflows.
Single-Cell Antibody Discovery Kits – Turnkey kits with Nanovials and all the reagents you need to perform antibody discovery workflows for plasma B cells or hybridomas. Just bring your cells and your antigens!
Multicell Antibody Discovery Kits – Tackle challenging antigens by pairing antigen expressing cells and antibody secreting cells. Kits include multicell Nanovials and antibodies for cell capture and IgG detection.
3. Instrumentation and Compatibility
Do I need to buy an instrument to perform Nanovial assays?
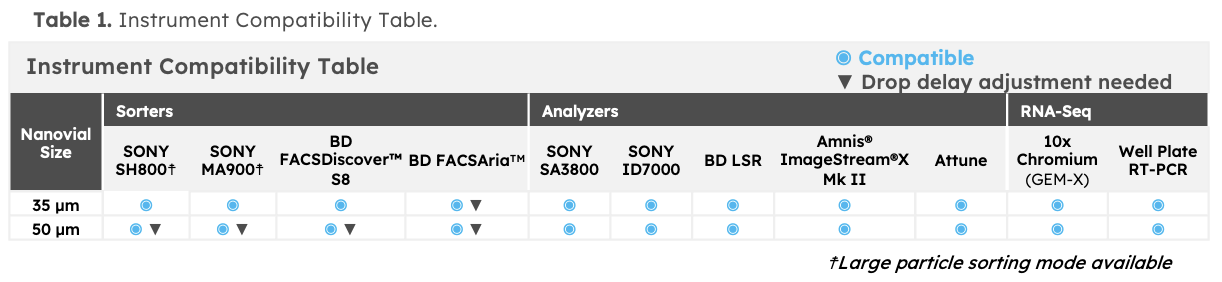
Nanovials were designed to be compatible with existing flow cytometry instruments and sequencing assays. The Nanovial workflow is performed with pipetting steps and uses common benchtop equipment such as a centrifuge and rotator. Flow cytometry can be used to sort cells based on functional readout. Cell loaded Nanovials can be put directly into plate-based or droplet-based single cell sequencing assays. Refer to the compatibility table for a list of common instruments. If your instrument does not appear on the table, reach out to us at support@partillion.com.
What flow sorters are compatible with Nanovials?
If your instrument does not appear on the table, reach out to us at support@partillion.com.
4. Assay Workflow: Staining, Recovery & Readouts
Can I recover cells from Nanovials after sorting for downstream experiments?
Yes! Cells remain viable after functional screening and sorting.
You can continue to use cell-loaded Nanovials for additional functional assays or sequencing. As the cavity remains open, you can perform reagent exchanges and reactions without having to remove cells from Nanovials.
Cell-loaded Nanovials can be cultured until cells grow out. Cells can then be separated using a cell strainer.
For adherent or ECM-bound cells, you can enzymatically release them (e.g., collagenase or trypsin) followed by straining.
Can I use viability dyes, surface markers, or reporter stains in Nanovial assays?
You can include additional stains during the staining step to add specificity for your flow cytometry readout or sorting. This includes:
Cell surface markers
Viability dyes (e.g., calcein-AM family, PI, DAPI)
Reporter stains or other functional markers
We generally recommend avoiding fixable viability dyes, as they may bind proteins on the Nanovial surface. Your kit protocol or our support team can suggest compatible dyes for your panel. As always, follow best practices for building a fluorophore panel for flow cytometry.
Can I measure more than one secreted protein at a time?
Nanovials can be functionalized with multiple capture antibodies so you can measure several secreted proteins in the same assay. We typically run up to three targets in parallel. Higher plex is possible but may reduce sensitivity. Talk to our team to design a panel that fits your application.
Can I look at interactions between two or more cells?
Yes! Multicell Antibody Discovery Kits and Developer Kits allow you to co-load two cell types into larger 50 µm Nanovials so you can study their interactions in the same particle.
For example, you can pair:
Jurkat T cells with Raji target cells to study killing or activation
Primary human T cells with adherent tumor cells to measure functional responses
CHO cells with Jurkat or HEK reporter cells for functional antibody library screening
Cancer cells with fibroblasts, or HEK cells with Jurkat reporters to probe signaling and paracrine effects
These assays let you measure outcomes such as antibody binding, target cell killing, reporter activation, or transcriptional changes at high throughput, and you can sort and further analyze the most interesting cell pairs.
Can I combine Nanovial-based assays with single-cell sequencing?
Cell-loaded Nanovials can be fed directly into plate-based or droplet-based single-cell sequencing workflows so you can analyze the transcriptomes of functionally interesting cells.
You can also add an extra layer of information with the SEC-seq (secretion-encoded single-cell sequencing) workflow. In SEC-seq, oligo-barcoded antibodies label the secretion signal on each Nanovial and are sequenced along with the cell’s mRNA, allowing you to link secretion phenotypes to gene expression at the single-cell level.
For cell–cell sequencing applications, Nanovials can hold defined cell pairs (for example, an effector and a target cell). You can then sequence these co-loaded pairs to measure transcriptional responses that arise from direct cellular interactions, providing a detailed view of how each cell type responds in the context of its partner (Cell-Cell Seq).
5. Performance and Advantages
How many cells can I screen in a single experiment?
Partillion products are built for high throughput. Each kit contains millions of Nanovials, and you can scale reactions by increasing the volume of Nanovials used. This enables screening of hundreds of thousands to millions of cells per experiment, depending on your assay and instrument. This throughput is a major advantage over traditional plate-based assays and many microfluidic systems.
What advantages do Partillion products offer over traditional methods?
Compared to plate-based or droplet-based systems, the Nanovial platform and its kits offer:
High throughput: Screen hundreds of thousands to millions of cells in a single tube.
Function + identity: Directly link secretions to the cell that produced them, and further interrogate hits with single-cell sequencing assays.
Live cell recovery: Sort and recover viable cells for downstream culture, engineering, or sequencing.
No specialized instruments required: Run Nanovial assays on standard flow cytometers and sorters—no complex microfluidics or expensive new hardware needed.
Multicell context with an easy upgrade path: Multicell assays let you study cell–cell interactions in a highly scalable format, and they use the same core workflow as single-cell Nanovial assays, making it simple to transition from single-cell to multicell experiments.